-
B-Tree - 삭제컴퓨터 구조 2021. 1. 18. 01:38

B-Tree - 삭제
B Tree 삽입에서 가득 찬 노드들을 미리 분할했던 것 처럼, 삭제시에도 최소 키의 개수를 가지는 노드들이 키를 더 많이 가질 수 있도록 미리 처리한다. k를 찾아 재귀적으로 내려가는 과정에서 방문하는 경로에 존재하는 키의 개수가 (t-1)인 경우 형제 노드에서 키를 가져오거나, 형제노드와 병합하는 과정을 거친다.
삭제 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 모든 경우의 수에 대해 알아보자.
1. 리프 노드 x를 방문했을 때, x 내에 k가 존재한다.
2. 리프 노드가 아닌 노드 x를 방문했을 때, x 내에 k가 존재한다.
3. 리프 노드가 아닌 노드 x를 방문했을 때, x 내에 k가 존재하지 않는다.
1. 리프 노드 x를 방문했을 때, x 내에 k가 존재한다.

리프 노드 x 내에 k가 존재한다면, k를 삭제한다.
x를 방문했다는 것은 이미 x에 존재하는 키의 개수가 t-1개보다 크다는 의미이기 때문에, 키 한 개를 삭제하더라도, 트리의 규칙에 어긋나지 않는다.
2. 리프 노드가 아닌 노드 x를 방문했을 때, x 내에 k가 존재한다.
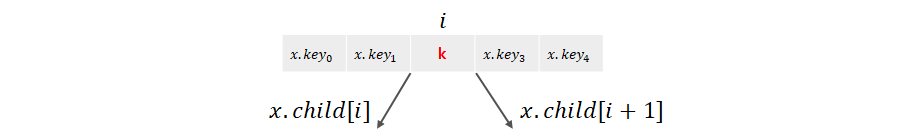
2 - 1. k가 i번째 키일 때, i번째 자식의 키의 개수가 t개 이상인 경우
k가 i번재 키일 때, i번째 자식의 키의 개수가 t개 이상인 경우(t-1개가 아닌 경우) x.child[i]를 루트로 하는 서브트리에서 가장 큰 수인 k`을 찾는다.
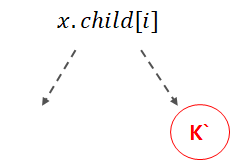
k`은 서브트리의 리프 노드들 중 가장 오른쪽에 위치한다. k`은 k 왼쪽에 위치한 수들 중 가장 큰 수이기 때문에 k대신 i번째 자식과 i+1번째 자식을 나누는 기준이 될 자격을 갖춘 수이다.
k`을 k자리에 대체한 후, x.child[i]로 내려가 k`을 재귀적으로 삭제한다.
재귀함수를 호출시켜 k를 삭제한다. Delete(x.child[i], k)를 실행하자.
2-2. k가 i번째 키일 때, i번째 자식의 키의 개수가 t-1개 이고, i+1번째 자식의 키의 개수는 t개 이상인 경우
k가 i번재 키일 때, i+1번째 자식의 키의 개수가 t개 이상인 경우(t-1개가 아닌 경우) x.child[i+1]를 루트로 하는 서브트리에서 가장 작은 수인 k`을 찾는다.
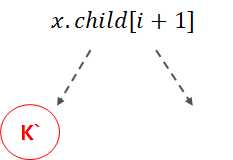
k`은 서브트리의 리프 노드들 중 가장 왼쪽에 위치한다. k`은 k 오른쪽에 위치한 수들 중 가장 작은 수이기 때문에 k대신 i번째 자식과 i+1번째 자식을 나누는 기준이 될 자격을 가지고 있다.
k`을 k자리에 대체한 후, x.child[i+1]로 k`을 삭제하러 재귀적으로 내려가자.
재귀함수를 호출시켜 k를 삭제한다. Delete(x.child[i+1], k)를 실행하자.
2-3. k가 i번째 키이고, i번째 자식과 i+1번째 자식의 키의 개수가 모두 t-1개인 경우


병합 i번째 자식과 k 그리고 i+1번째 자식을 합쳐, 2t-1개의 키를 가지는 새로운 노드를 만든다.
t-1개의 키를 가지는 두개의 노드와 k를 합쳤기 때문에 이 경우 병합된 노드에 존재하는 키의 개수는 항상 2t-1개이다.

이렇게 노드에 존재하는 키의 개수를 보충해 주고, 자식 노드로 k를 지우러 가는 재귀함수를 실행시키자.
3. 리프 노드가 아닌 노드 x를 방문했을 때, x 내에 k가 존재하지 않는다.
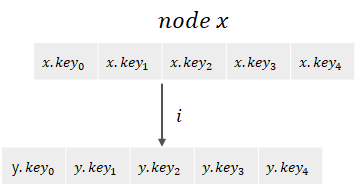
k가 x내에 존재하지 않는다면, k가 위치해야 하는 자식 노드의 위치를 먼저 찾는다. 이때, 자식 노드(i번째 자식)와 형제 노드들의 키의 개수에 따라 경우가 나뉜다.
3 - 1. i번째 자식 노드에 존재하는 키의 개수가 t개 이상인 경우

i번째 자식 노드로 k를 삭제하러 가기 위한 재귀함수를 실행시킨다.
3 - 2. i번째 자식 노드에 존재하는 키의 개수가 t-1개인 경우
3-2-1. i-1번째 자식 노드에 존재하는 키의 개수가 t개 이상인 경우 i-1번째 자식 노드로부터 키 한 개를 빌려오자.

3-2-2. i+1번째 자식 노드에 존재하는 키의 개수가 t개 이상인 경우 i+1번째 자식 노드로부터 키 한 개를 빌려오자.
3-2-3. 양 옆의 형제노드 모두 키의 개수가 t-1개인 경우 왼쪽 혹은 오른쪽 형제노드와 병합한다. child[i]와 child[i+1]을 병합하는 경우 i 번째 key도 함께 병합한다. 2-3의 경우와 같이 t-1개의 노드 두개와 키 한개를 병합하기 때문에, 2t-1개의 키를 가지게 된다.
Code
더보기/* * Btree example * * * 20210109, youseop, jeongseo, gojae * * */ /* * * 1. 모든 리프노드는 트리 높이(h)와 같은 깊이에 있다. * 2. t-1 <= 키의 개수 <= 2t-1 * 2-1 루트 노드의 키의 개수는 t-1개 보다 적을 수 있다. * 3. 리프 노드가 아닐 경우, 키의 개수 +1개 = 자식의 개수 <= 2t * */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define EMPTY 0 #define DEGREE 2 /*The degree of the tree.*/ typedef struct node { int key[2 * DEGREE - 1]; struct node* child[2 * DEGREE]; int leaf; int n; } node; typedef struct B_Tree { node* root; }B_Tree; void B_Tree_Create(B_Tree* T); void B_Tree_Insert(B_Tree* T, int k); void B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(node* x, int k); int B_Tree_Search(B_Tree* T, int k); int B_Tree_Search_Main(node* x, int k); void B_Tree_Split_Child(node* x, int i); void B_Tree_Display(B_Tree* T); void B_Tree_Display_Main(node* x, int h); void B_Tree_Delete(B_Tree* T, int k); void B_Tree_Delete_main(node* x, int k); int Find_Successor(node* x); int Find_Predecessor(node* x); void B_Tree_insert_items(B_Tree* T, int x, int y); void main() { B_Tree* T = malloc(sizeof(B_Tree)); B_Tree_Create(T); xx->child[1] = z; int command, x, y; printf("##########################\n\n $ B_TREE Project $ \n\nproduced by \n\n@jeongseo \n@youseop \n@gojae\n\n##########################\n\n"); while (1) { printf("\n1: insert one item\n2: insert items (x~y)\n3: delete item\n4: display\ncommad: "); scanf("%d", &command); if (command == 1) { printf("insert item: "); getchar(); scanf("%d", &x); B_Tree_Insert(T, x); B_Tree_Display(T); } else if (command == 2) { printf("\ninsert x & y\n (y should be bigger than x)\nx: "); getchar(); scanf("%d", &x); printf("y: "); getchar(); scanf("%d", &y); B_Tree_insert_items(T, x, y); } else if (command == 3) { printf("\ninsert a number you wanna delete.\nk : "); getchar(); scanf("%d", &x); B_Tree_Delete(T, x); B_Tree_Display(T); } else if (command == 4) { B_Tree_Display(T); } else if (command == 0) { break; } getchar(); } free(T); } void B_Tree_insert_items(B_Tree* T, int x, int y) { for (int i = x; i < y + 1; i++) { B_Tree_Insert(T, i); } B_Tree_Display(T); } void B_Tree_Create(B_Tree* T) { node* x = malloc(sizeof(node)); if (x == NULL) { printf("memory allocation falied"); return; } x->leaf = TRUE; x->n = 0; T->root = x; } void B_Tree_Insert(B_Tree* T, int k) { node* r = T->root; if (r->n == 2 * DEGREE - 1) { node* s = malloc(sizeof(node)); if (s == NULL) { printf("memory allocation falied"); return; } T->root = s; s->leaf = FALSE; s->n = 0; s->child[0] = r; B_Tree_Split_Child(s, 0); B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(s, k); //printf("insert %d\n", k); } else { B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(r, k); } } void B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(node* x, int k) { int i = x->n; if (x->leaf) { i--; while (i >= 0 && k < x->key[i]) { x->key[i + 1] = x->key[i]; i--; } x->key[i + 1] = k; x->n = x->n + 1; } else { while (i >= 1 && k < x->key[i - 1]) { i--; } if ((x->child[i])->n == 2 * DEGREE - 1) { B_Tree_Split_Child(x, i); if (k > x->key[i]) { i++; } } //printf("child#: %d k: %d\n", i, k); B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(x->child[i], k); } } int B_Tree_Search(B_Tree* T, int k) { node* r = T->root; return B_Tree_Search_Main(r, k); } //함수 수정 필요! int B_Tree_Search_Main(node* x, int k) { if (x->leaf) { int i = x->n - 1; while (i >= 0 && k < x->key[i]) { i--; } if (x->key[i] == k) { printf("There is data\n"); return TRUE; } else { printf("No data\n"); return FALSE; } } } void B_Tree_Split_Child(node* x, int i) { node* z = malloc(sizeof(node)); if (z == NULL) { printf("memory allocation falied"); return; } node* y = x->child[i]; // 0 <= i z->leaf = y->leaf; z->n = DEGREE - 1; for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE - 1; j++) { z->key[j] = y->key[j + DEGREE]; } if (y->leaf == FALSE) { for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE; j++) { z->child[j] = y->child[j + DEGREE]; } } y->n = DEGREE - 1; for (int j = x->n; j > i; j--) { x->child[j + 1] = x->child[j]; } x->child[i + 1] = z; for (int j = x->n - 1; j > i - 1; j--) { x->key[j + 1] = x->key[j]; } x->key[i] = y->key[DEGREE - 1]; x->n = x->n + 1; } void B_Tree_Display(B_Tree* T) { node* r = T->root; B_Tree_Display_Main(r, 1); } void B_Tree_Display_Main(node* x, int h) { printf("%d : ", h); for (int i = 0; i < x->n; i++) { printf("%d ", x->key[i]); } printf("\n"); if (x->leaf == 0) { for (int i = 0; i < x->n + 1; i++) { B_Tree_Display_Main(x->child[i], h + 1); } } } void B_Tree_Delete(B_Tree* T, int k) { node* r = T->root; int i = r->n - 1; if (r->leaf == 1) { while (i >= 0 && r->key[i] > k) { i--; } if (i >= 0 && r->key[i] == k) { for (int j = i + 1; j < r->n; j++) { r->key[j - 1] = r->key[j]; } r->n--; printf("delete success\n"); } else { printf("no data"); } return; } else { if (r->n > 1) { B_Tree_Delete_main(r, k); } else { node* left_c = r->child[0]; node* right_c = r->child[1]; if (left_c->n == DEGREE - 1 && right_c->n == DEGREE - 1) { left_c->key[DEGREE - 1] = r->key[0]; for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE - 1; j++) { left_c->key[DEGREE + j] = right_c->key[j]; } if (left_c->leaf == FALSE) { for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE; j++) { left_c->child[DEGREE + j] = right_c->child[j]; } } left_c->n = DEGREE * 2 - 1; free(right_c); T->root = left_c; free(r); B_Tree_Delete_main(left_c, k); } else { B_Tree_Delete_main(r, k); } } } } void B_Tree_Delete_main(node* x, int k) { printf("star %d\n", k); int i = x->n; while (i > 0 && x->key[i - 1] >= k) { i--; } if (i < x->n && x->key[i] == k) { if (x->leaf == 1) { for (int j = i; j < x->n - 1; j++) { x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1]; } x->n--; return; } else { printf("no leaf\n"); node* left_c = x->child[i]; node* right_c = x->child[i + 1]; if (left_c->n > DEGREE - 1) { printf("here?\n"); int pre_k = Find_Predecessor(left_c); printf("%d\n", pre_k); x->key[i] = pre_k; B_Tree_Delete_main(left_c, pre_k); } else if (right_c->n > DEGREE - 1) { int su_k = Find_Successor(right_c); x->key[i] = su_k; B_Tree_Delete_main(right_c, su_k); } else { left_c->key[DEGREE - 1] = k; for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE - 1; j++) { left_c->key[DEGREE + j] = right_c->key[j]; } for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE; j++) { left_c->child[DEGREE + j] = right_c->child[j]; } left_c->n = 2 * DEGREE - 1; for (int j = i; j < x->n - 1; j++) { x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1]; } for (int j = i + 1; j < x->n; j++) { x->child[j] = x->child[j + 1]; } x->n--; free(right_c); B_Tree_Delete_main(left_c, k); } } } else { node* my_way_c = x->child[i]; if (my_way_c->n > DEGREE - 1) { B_Tree_Delete_main(my_way_c, k); } else { if (i != 0 && (x->child[i - 1])->n > DEGREE - 1) { node* left_c = x->child[i - 1]; for (int j = DEGREE - 2; j >= 0; j--) { left_c->key[j + 1] = left_c->key[j]; } if (left_c->leaf == FALSE) { for (int j = DEGREE - 1; j >= 0; j--) { left_c->child[j + 1] = left_c->child[j]; } } my_way_c->key[0] = x->key[i - 1]; my_way_c->child[0] = left_c->child[left_c->n]; my_way_c->n++; x->key[i - 1] = left_c->key[left_c->n - 1]; left_c->n--; } else if (i != x->n && (x->child[i + 1])->n > DEGREE - 1) { node* right_c = x->child[i + 1]; my_way_c->key[DEGREE - 1] = x->key[i]; my_way_c->child[DEGREE] = right_c->child[0]; my_way_c->n++; x->key[i] = right_c->key[0]; for (int j = 0; j < right_c->n - 1; j++) { right_c->key[j] = right_c->key[j + 1]; } for (int j = 0; j < right_c->n; j++) { right_c->child[j] = right_c->child[j + 1]; } right_c->n--; } else {//x에 k가 없고, 풍족한 형제가 없을때!!! if (i == 0) { node* right_c = x->child[i + 1]; for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE - 1; j++) { right_c->key[j + DEGREE] = right_c->key[j]; right_c->key[j] = my_way_c->key[j]; } if (right_c->leaf == 0) { for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE; j++) { right_c->child[j + DEGREE] = right_c->child[j]; right_c->child[j] = my_way_c->child[j]; } } right_c->key[DEGREE - 1] = x->key[i]; right_c->n = DEGREE * 2 - 1; for (int j = 0; j < x->n - 1; j++) { x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1]; } for (int j = 0; j < x->n; j++) { x->child[j] = x->child[j + 1]; } free(my_way_c); my_way_c = right_c; x->n--; } else { node* left_c = x->child[i - 1]; left_c->key[DEGREE - 1] = x->key[i - 1]; for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE - 1; j++) { left_c->key[j + DEGREE] = my_way_c->key[j]; } if (left_c->leaf == 0) { for (int j = 0; j < DEGREE; j++) { left_c->child[j + DEGREE] = my_way_c->child[j]; } } left_c->n = 2 * DEGREE - 1; for (int j = i - 1; j < x->n - 1; j++) { x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1]; } for (int j = i; j < x->n; j++) { x->child[j] = x->child[j + 1]; } free(my_way_c); my_way_c = left_c; x->n--; } } B_Tree_Delete_main(my_way_c, k); } } return; } int Find_Predecessor(node* x) { while (x->leaf == 0) { x = x->child[x->n]; } return x->key[x->n - 1]; } int Find_Successor(node* x) { while (x->leaf == 0) { x = x->child[0]; } return x->key[0]; }'컴퓨터 구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
Thread ( + pthread) (0) 2021.01.23 pointer & memory segment (0) 2021.01.18 B-Tree - 삽입 (0) 2021.01.13 B-Tree - intro (1) 2021.01.11 단순 연결 리스트 (0) 2021.01.10